- 70855-06939
- drponamrathod025@gmail.com
- Sandeep Vihar Society ,GH 79, Sect 20, Panchkula
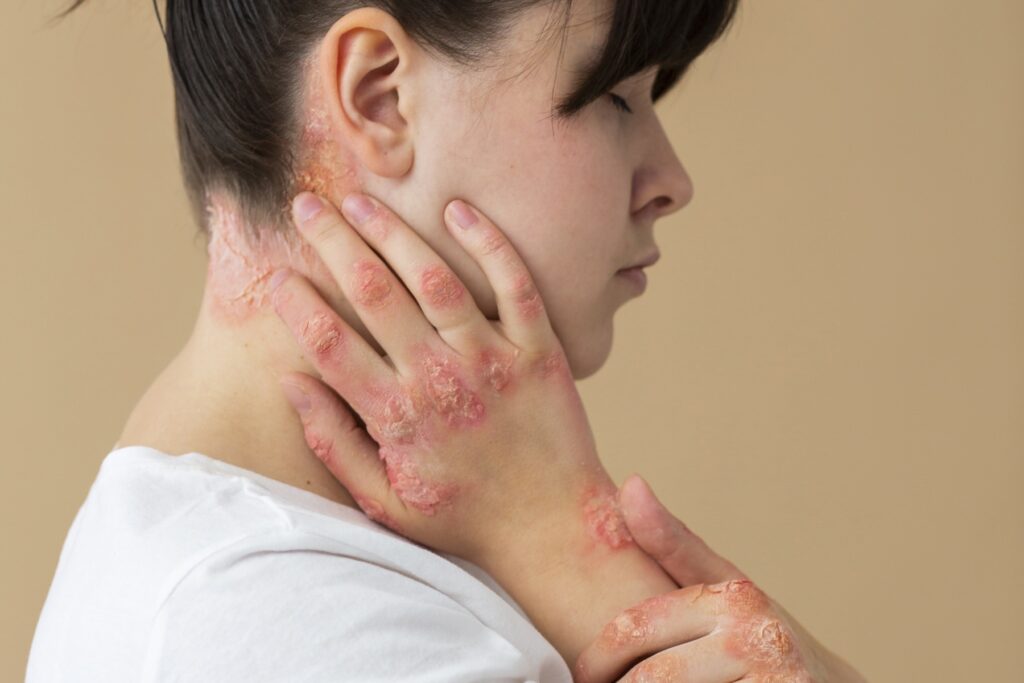
Psoriasis Treatment
Psoriasis, a chronic autoimmune condition, affects the skin by causing rapid skin cell turnover, leading to red, inflamed patches covered with silvery-white scales. This disorder impacts more than just the skin, often leading to emotional and psychological challenges. A deeper understanding of psoriasis, its triggers, and treatment modalities can empower individuals to take proactive steps toward managing the condition effectively.
What Is Psoriasis?
Psoriasis is an immune-mediated disease where the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks healthy skin cells. Psoriasis overactive immune response causes the skin to regenerate faster than normal, leading to the accumulation of cells on the skin’s surface. The condition can occur at any age, though it commonly develops between 15 and 35 years of age. Psoriasis is not contagious, but it can run in families, pointing to a genetic predisposition.
Common Triggers for Psoriasis
Several factors can trigger or worsen psoriasis, and these vary from person to person. Common triggers include:
- Stress: High stress levels can provoke or intensify flare-ups.
- Weather Conditions: Cold and dry weather often worsens symptoms, while warm, sunny climates may improve them.
- Infections: Conditions such as strep throat are known to trigger guttate psoriasis.
- Skin Trauma: Cuts, burns, or bug bites can lead to new lesions (Koebner phenomenon).
- Medications: Drugs like lithium, beta-blockers, and antimalarials can exacerbate psoriasis.
- Lifestyle Factors: Smoking and excessive alcohol consumption are associated with more severe symptoms.
Symptoms: Beyond the Skin
While psoriasis primarily affects the skin, its impact can extend to other areas of health:
- Skin Symptoms: Raised, red patches with silvery scales, itching, burning, or soreness.
- Nail Symptoms: Pitting, discoloration, and separation of nails from the nail bed.
- Joint Symptoms: Pain, swelling, and stiffness associated with psoriatic arthritis, a condition that affects up to 30% of people with psoriasis.
Types of Psoriasis
Understanding the specific type of psoriasis is crucial for effective treatment:
- Plaque Psoriasis: The most common form, accounting for about 80-90% of cases.
- Guttate Psoriasis: Appears as small, teardrop-shaped lesions, often triggered by infections.
- Inverse Psoriasis: Found in skin folds, such as under the breasts or around the groin.
- Pustular Psoriasis: Characterized by white pustules surrounded by red skin.
- Erythrodermic Psoriasis: A severe, life-threatening type that causes widespread redness and shedding.
Treatment Modalities for Psoriasis
1. Medical Treatments
Psoriasis treatments aim to manage symptoms, reduce inflammation, and prevent flare-ups. Options include:
- Topical Treatments:
- Corticosteroids: Effective in reducing inflammation and itching.
- Vitamin D Analogues: Help slow skin cell growth.
- Salicylic Acid: Removes scales and promotes smoother skin.
- Coal Tar: Reduces itching and inflammation.
- Phototherapy:
- Involves exposing the skin to controlled ultraviolet (UV) light, which can slow down cell production and reduce inflammation.
- Systemic Medications:
- Methotrexate and cyclosporine: Suppress immune system overactivity.
- Biologic Therapies: Target specific immune responses involved in psoriasis, offering precision treatment.
2. Natural and Alternative Approaches
- Dietary Changes: Anti-inflammatory diets rich in fruits, vegetables, omega-3 fatty acids, and whole grains may help manage symptoms.
- Stress Management: Techniques such as yoga, meditation, and mindfulness can help reduce stress-related flare-ups.
- Hydration: Moisturizers keep skin hydrated and reduce scaling.
- Herbal Remedies: Ingredients like aloe vera and turmeric are known for their soothing and anti-inflammatory properties.
3. Lifestyle Adjustments
- Quitting Smoking: Smoking can worsen psoriasis and reduce treatment effectiveness.
- Limiting Alcohol: Reducing alcohol intake can lower inflammation levels.
- Exercise: Regular physical activity helps maintain overall health and reduce stress.
Managing Psoriasis Holistically
Beyond treating physical symptoms, addressing the emotional and psychological impact of psoriasis is critical:
- Mental Health Support: Psoriasis can lead to anxiety, depression, and social withdrawal. Seeking counseling or joining support groups can help.
- Education and Awareness: Learning more about psoriasis empowers individuals to take control of their condition and advocate for appropriate care.
- Routine Dermatological Checkups: Regular visits to a dermatologist ensure that treatment plans remain effective and up-to-date.
Outlook for Psoriasis
Although psoriasis is a lifelong condition, advances in treatment and management techniques offer hope for individuals to lead fulfilling lives. With the right combination of medical care, lifestyle changes, and emotional support, most people with psoriasis can achieve significant symptom control and improved quality of life. Early intervention and proactive management are key to minimizing its impact.
Menu
